Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud Networking
Objectives: Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud Networking, The Different Between Virtual Private Network and Direct Connect.
1. Hybrid
Cloud and Multi-Cloud Networking
The purpose for
this blog article is to discuss some helpful tips regarding hybrid cloud and
multi-cloud networking, and the differences between VPN (Virtual Private
Network) and Direct Connect – the important role both methods play in connecting
network. A hybrid cloud is a network infrastructure that exists in two
different places – on-prem and in the cloud. Like hybrid clouds is multi-cloud
which is a network infrastructure that’s dedicated to two or many different
platforms like, AWS (Amazon Web Service), GCP (Google Cloud Platform), or
Microsoft Azure and Salesforce. With all these different platforms, one could wonder
about the notable complexity in making these different network services and tools
to communicate to and assist each other. The question then is, so why will any
organization establish such metaphorical giant? The overall ideal answer to
this “is that hybrid and multi-clouds are becoming more reasonable and popular
due to their flexibility and potential cost benefits. A hybrid cloud is a
typical transition phase as companies migrate to the cloud, and many companies
ultimately decide to continue indefinitely with a hybrid infrastructure.”
2. Different
Between Virtual Private Network
VPN (Virtual
Private Network) is a networking method used purposefully for establishing
secured (encrypted) pathway (tunnel) for the safe travels of traffic over
public Internet connection – meaning that there is a possibility for “latency”
to become a problem based on “Internet weather conditions.” In some cases, SLA
(Service Lever Agreement) might not cover Internet connection availability, however,
the guarantee for high availability is possible with the creations and maintenance
of several VPN connections. Alternatively, just as VPN tunnel can be creates to
across public Internet, so as private Internet where an ISP (Internet Service
Provider) will provide “MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) connection,” that’s
pricey.
To assist with
cloud-based VPN network connection for users working remotely, a “VPN endpoint resource”
must be configurated in VPC (Virtual Private Cloud). By configurating VPC, you
will have the ability for sending “client configuration file” to remote users who
want to install the VPN application on their machine (computer). One of several
important aspects to understand is that VPN services will automatically scale
as demand for use increases or decreases. In addition, charges apply “connection-hours.”
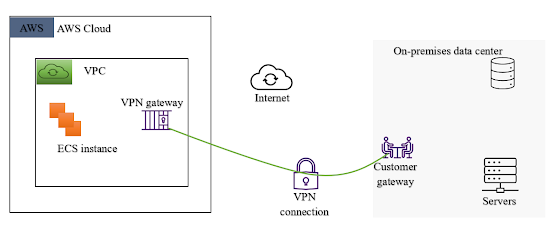
If an organization were establishing a connection from its data center
(headquarter) in Trenton, NJ, and to its VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) on Azure
or AWS platform, for such connection to be a success, for example, the
organization will “need a CGW (customer gateway)” device in their Trenton, NJ
“network and a VGW (virtual gateway) service running on” their VPC as shown in
the diagram below courtesy of CompTIA Cloud+ Guide to Cloud Computing.
3. Direct
Connect
Unlike VPN that’s
inexpensive and provided relatively secure connection to network cloud
resources, and low-speed connection, direct connect on the other hand is known
for its high-speed connection, low-latency, a variety of characteristics and services
base on providers, and far more security mode, but expensive. In the context of
cloud networks, VPNs are often used to connect a single device to cloud
resources or to connect a cloud network to an on-prem network over the public
Internet. Whereas in context, a direct connection is far more balanced used
devoted private infrastructure when connecting to an on-prem data center (network)
through the infrastructure of a CSP (Cloud Service Provider). If you want to establish
a direct connection from a data center to a public cloud, you can accomplish
this simply by converting with a “CSP in a location called a col or colo (colocation).”
In computer networking “colo is a data center facility” that’s dedicated to
specifically to “interconnecting services providers, (both ISPs and CSPs) with
their business partners and customers.” As a cloud user, you are allowed the
option to ask for or demand direct connection within that specific facility (building)
“to any number of service providers to support a hybrid or multi-cloud
deployment” as long you can establish connection to the colo.
Listed below is
a diagram of a colocation facility that establishes direct connections between
service providers and their customers – courtesy of CompTIA Cloud+ Guide to
Cloud Computing.
References:
West, Jill. (2023).
CompTIA Cloud+ Guide to Cloud Computing (p.171-176). Kindle Edition. Retrieved:
October 17, 2023.

Comments
Post a Comment